JavaScript offers a bunch of useful array methods to check whether an array contains a particular value.
While searching for primitive value like number or string is relatively easy, searching for objects is slightly more complicated.
In this post, you will read about how to determine if an array contains a particular value, being a primitive or object.
1. Array contains a primitive value
A primitive value in JavaScript is a string, number, boolean, symbol, and special value undefined.
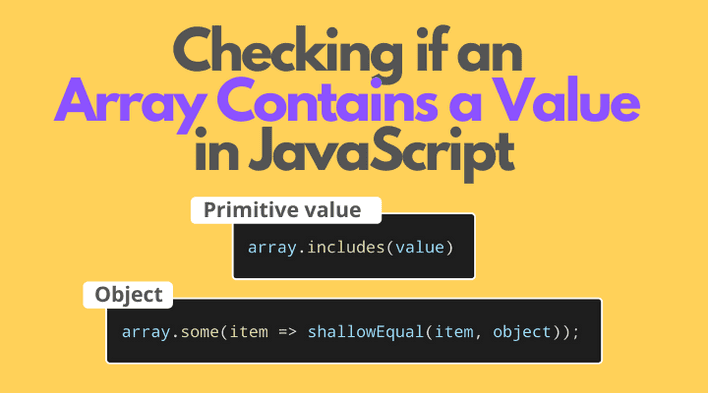
The easiest way to determine if an array contains a primitive value is to use array.includes() ES2015 array method:
const hasValue = array.includes(value[, fromIndex]);
The first argument value is the value to search in the array. The second, optional, argument fromIndex is the index from where to start searching. The method returns a boolean indicating whether array contains value.
For example, let's determine whether an array of greeting words contains the values 'hi' and 'hey':
const greetings = ['hi', 'hello'];greetings.includes('hi'); // => truegreetings.includes('hey'); // => false
greetings.includes('hi') returns true because the array contains 'hi' item.
But greetings.includes('hey') returns false, denoting that 'hey' is missing in the greetings array.
1.1 Searching from an index
array.includes(value, fromIndex) also accepts an optional second argument to start search for value starting an index.
For example, let's start searching from the second item (index 1 and up) in the array:
const letters = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];letters.includes('c', 1); // => trueletters.includes('a', 1); // => false
letters.includes('c', 1) starts searching for 'c' letter from index 1. As expected, the letter is found.
However, letters.includes('a', 1) returns false because the array from index 1 until the end doesn't contain the item 'a'.
2. Array contains an object
Checking if an array contains an object is slightly more complex than searching for primitive values.
Determining if an array contains a reference to an object is easy — just use the array.includes() method. For example:
const greetings = [{ message: 'hi' }, { message: 'hello' }];const toSearch = greetings[0];greetings.includes(toSearch); // => true
greetings.includes(toSearch) returns true because the greetings array contains toSearch object reference (which points to the first item of the array).
But more often, instead of searching by reference, you'd like to search for objects by their content. In such a case array.includes() won't work:
const greetings = [{ message: 'hi' }, { message: 'hello' }];const toSearch = { message: 'hi' };greetings.includes(toSearch); // => false
greetings.includes(toSearch) returns false, because the array doesn't contain toSearch object reference. Although the array contains the object hi that looks exactly like toSearch.
Ok, so how do you determine if the array contains an object by content, rather than reference? Using array.some() method in combination with shallow or deep equality check of objects.
During shallow equality check of objects the list of properties of both objects is checked for equality.
Here's a possible implementation of shallow equality check:
function shallowEqual(object1, object2) { const keys1 = Object.keys(object1); const keys2 = Object.keys(object2); if (keys1.length !== keys2.length) { return false; } for (let key of keys1) { if (object1[key] !== object2[key]) { return false; } } return true;}
shallowEqual(object1, object2) returns true in case if both compared objects object1 and object2 have the same set of properties with the same values.
In the following code snippet hi and hiCopy are equal by content, while hi and hello are not:
const hi = { message: 'hi' };const hiCopy = { message: 'hi' };const hello = { message: 'hello' };shallowEqual(hi, hiCopy); // => trueshallowEqual(hi, hello); // => false
As a reminder, the array method array.some(callback) returns true if at least one time callback function returns true.
Now, let's use the shallow equality function in combination with array.some(callback) method to find if the array contains an object by content:
const greetings = [{ message: 'hi' }, { message: 'hello' }];const toSearch = { message: 'hi' };greetings.some(item => shallowEqual(item, toSearch)); // => true
greetings.some(item => shallowEqual(item, toSearch)) checks every item of the array for shallow equality with toSearch object.
If the searched object contains also nested objects, then instead of shallowEqual() function you could use the deepEqual() function.
3. Summary
Searching for a primitive value like string or number inside of an array is simple: just use array.includes(value) method.
Determining if an array contains an object by content needs more moving parts. You have to use array.some(callback) method combined with shallow equality check:
array.some(item => shallowEqual(item, value));
Note that the presented approaches are not the only ones. E.g. for a long time array.indexOf(value) !== -1 expression (which is slighlty clumsy) has been used to determine if the array contains value.
What other ways to detect if an array contains a value do you know?