A Uniform Resource Locator, abbreviated URL, is a reference to a web resource (web page, image, file). The URL specifies the resource location and a mechanism to retrieve the resource (http, ftp, mailto).
For example, here's the URL of this blog post:
https://dmitripavlutin.com/parse-url-javascript
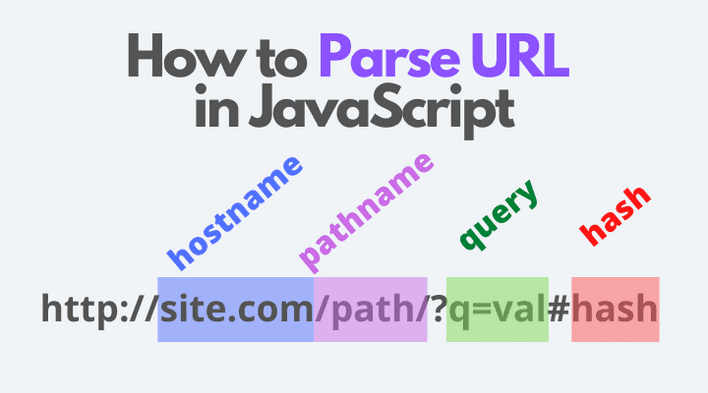
Often you need to access specific components of an URL: the hostname (e.g. dmitripavlutin.com), or pathname (e.g. /parse-url-javascript).
A convenient parser to access components of an URL is the URL() constructor.
In this post, I'm going to show you the structure of an URL and its main components. Then, I'm going to describe how to use the URL() constructor to easily pick components of an URL like hostname, pathname, query, or hash.
Table of Contents
1. URL structure
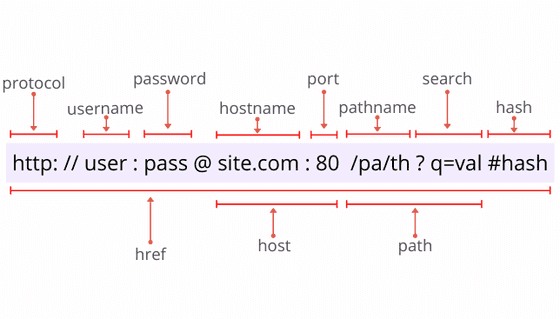
An image worth a thousand words. Without much textual description, in the following image you can find the main components of an URL:
2. URL() constructor
The URL() is a constructor function to parse components of an URL:
const url = new URL(relativeOrAbsolute [, absoluteBase]);
relativeOrAbsolute argument can be either an absolute or relative URL. If the first argument is relative, then the second argument absoluteBase is obligatory and must be an absolute URL being the base for the relative path.
For example, let's initialize URL() with an absolute URL:
const url = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html');console.log(url.href); // => 'http://example.com/path/index.html'
or combine relative and absolute URLs:
const url = new URL('/path/index.html', 'http://example.com');console.log(url.href); // => 'http://example.com/path/index.html'
The href property of the URL() instance returns the entire URL string.
After creating an URL() instance, you can access any URL component presented in the previous picture. For reference, here's the URL() instance interface:
interface URL { href: USVString; protocol: USVString; username: USVString; password: USVString; host: USVString; hostname: USVString; port: USVString; pathname: USVString; search: USVString; hash: USVString; readonly origin: USVString; readonly searchParams: URLSearchParams; toJSON(): USVString;}
where USVString type maps to a string when returned in JavaScript.
3. Query string
url.search property accesses the query string of the URL (the one that starts with ?):
const url = new URL( 'http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world');console.log(url.search); // => '?message=hello&who=world'
If the query string is missing, url.search evaluates to an empty string '':
const url1 = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html');const url2 = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html?');console.log(url1.search); // => ''console.log(url2.search); // => ''
3.1 Parsing the query string
But more often you might need to access a specific query parameter.
An easy way to pick query parameters gives url.searchParams property. This property holds an instance of URLSearchParams.
URLSearchParams object provides lots of methods (like get(param), has(param)) to access the query string parameters.
Let's look at an example:
const url = new URL( 'http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world');console.log(url.searchParams.get('message')); // => 'hello'console.log(url.searchParams.get('missing')); // => null
url.searchParams.get('message') returns the value of message query parameter — 'hello'.
But accessing a non-existing parameter url.searchParams.get('missing') evaluates to null.
4. hostname
url.hostname property holds the hostname of the URL:
const url = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html');console.log(url.hostname); // => 'example.com'
5. pathname
url.pathname property accesses the pathname of the URL:
const url = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html?param=value');console.log(url.pathname); // => '/path/index.html'
If the URL doesn't have a path, the url.pathname property returns a slash character /:
const url = new URL('http://example.com/');console.log(url.pathname); // => '/'
6. hash
Finally, the hash is accessed using url.hash property:
const url = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html#top');console.log(url.hash); // => '#top'
When the hash in the URL is missing, url.hash evaluates to an empty string '':
const url = new URL('http://example.com/path/index.html');console.log(url.hash); // => ''
7. URL validation
When new URL() constructor creates an instance, as a side effect, it also validates
the URL for correctness. A TypeError is thrown if the URL value is invalid.
For example, http**://example.com is an invalid URL because of the ** characters after http.
Let's use this invalid URL to initialize the parser:
try { const url = new URL('http**://example.com');} catch (error) { console.log(error); // => TypeError, "Failed to construct URL: Invalid URL"}
Because 'http**://example.com' is an invalid URL, as expected, new URL('http**://example.com') throws a TypeError.
8. URL manipulation
Aside from accessing URL components, the properties like search, hostname, pathname, hash are writeable — thus you can manipulate the URL.
For example, let's modify the hostname of an existing URL from red.com to blue.io:
const url = new URL('http://red.com/path/index.html');console.log(url.href); // => 'http://red.com/path/index.html'url.hostname = 'blue.io';console.log(url.href); // => 'http://blue.io/path/index.html'
Only origin and searchParams properties of the URL() instance are readonly. The other ones are writable and modify the URL when you change them.
9. Summary
The URL() constructor is handy for parsing (and validating) URLs in JavaScript.
new URL(relativeOrAbsolute [, absoluteBase]) accepts as the first argument an absolute or relative URL. When the first argument is relative, you have to indicate the second argument as an absolute URL that serves as the base for the first argument.
After creating the URL() instance, you can easily access the most common URL components like:
url.searchfor raw query stringurl.searchParamsfor an instance ofURLSearchParamsto pick query string parametersurl.hostnameto access the hostnameurl.pathnameto read the pathnameurl.hashto determine the hash value
In terms of browser support, URL constructor is available in modern browsers. However, it is not available in Internet Explorer.
What is your favorite tool to parse URLs in JavaScript?